- Home
- About us
- Products
- COMPOSITES MATERIAL
- —fibreglass & carbon
- —infusion consumables
- —sandwich panels
- —GlossLamix™ skin sheet
- —EcoLamix™ skin sheet
- —MaxFloat™ syntactic foam
- 3S INDUSTRIAL LIFTING
- —blade maintain platform
- —ladder hoist
- WEARABLE EXOSKELETON
- —PES-B back suit
- —PES-U upper Limb Suit
- —FIT-HV lumbar exo
- —FIT-U upper limb exo
- Contact us
Discovery Composites Material
Sandwich Panels - Thermoplastic
Lightweight, High Stiffness, and Environmentally Sustainable
A sandwich-structured composite is normally consisting of two thin, stiff skins bonded to a thick, lightweight core. While the core material is typically of low strength, its thickness provides the composite with high bending stiffness while maintaining a low overall density.
Common core materials include open- or closed-cell foams such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane (PU), polyethylene (PET), balsa wood and honeycombs. Skins are typically made from glass or carbon fibre-reinforced laminates of thermoset polymers like unsaturated polyesters and epoxies.
With sustainability becoming a major global focus, a recent trend is the use of continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastics (CFRT) as the skin material, bonded to the core through a double belt hot pressing process. This approach not only improves manufacturing efficiency but also reduces energy consumption, while enhancing the recyclability of the panels, thanks to the thermoplastic properties. When both the skin matrix component and core materials are made from the same polymer base, such as PET, the recyclability is further increased.
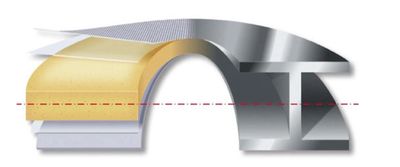

CFRT PET foam core sandwich panels
A full PET-based sandwich panel constructed with PET based CFRT (Continuous Fibreglass Reinforced Thermoplastic) skin and a PET extruded foam core, offering lightweight, high stiffness, super impact resistance, great insulation and superior recyclability.
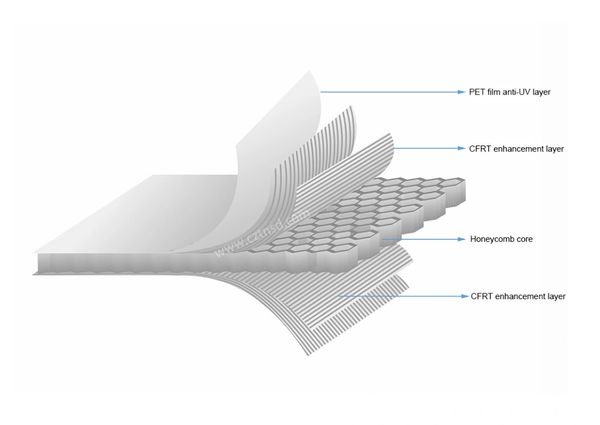
CFRT honeycomb core sandwich panels
A cost effective sandwich panel constructed with PET/PP based CFRT (Continuous Fibreglass Reinforced Thermoplastic) skin and a Polypropylene honeycomb core, providing lightweight, high stiffness and recyclability.
OTHER COMPOSITES MATERIAL PRODUCTS
Glass and Carbon Fibre
Glass and carbon uni-directional, Multi-axial, Chopped strand and continuous filament mat, etc.
Vacuum Infusion Process Consumables
Bagging films, Peel ply, Release film, Sealant tapes, Flow mesh, Tube and spiral hose
CFRT UD Prepreg Tape/Sheet
Continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastic polymer tapes and sheets
CONTACT US
This website uses cookies
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your browsing experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data